Introduce
During the spring flowering season, apple trees produce an excessive number of flower clusters, and if all these flowers bear fruit, the** fruit yield** is reduced and the size of the fruit is small. Immediate thinning of the excess flower clusters is an urgent activity in the orchard every year, as the flowering period is very short, lasting about a week. Currently, flower thinning is generally done manually, which requires a lot of labor in order to do it as quickly as possible. Flower thinning requires mastering how to select the best flower clusters for retention, which was usually taught on site by experienced staff in the past, but the results were often limited by the tight work schedule. Based on this, we propose to reconstruct the orchard in a virtual environment, so that new employees can learn to master flower thinning skills in a VR environment.

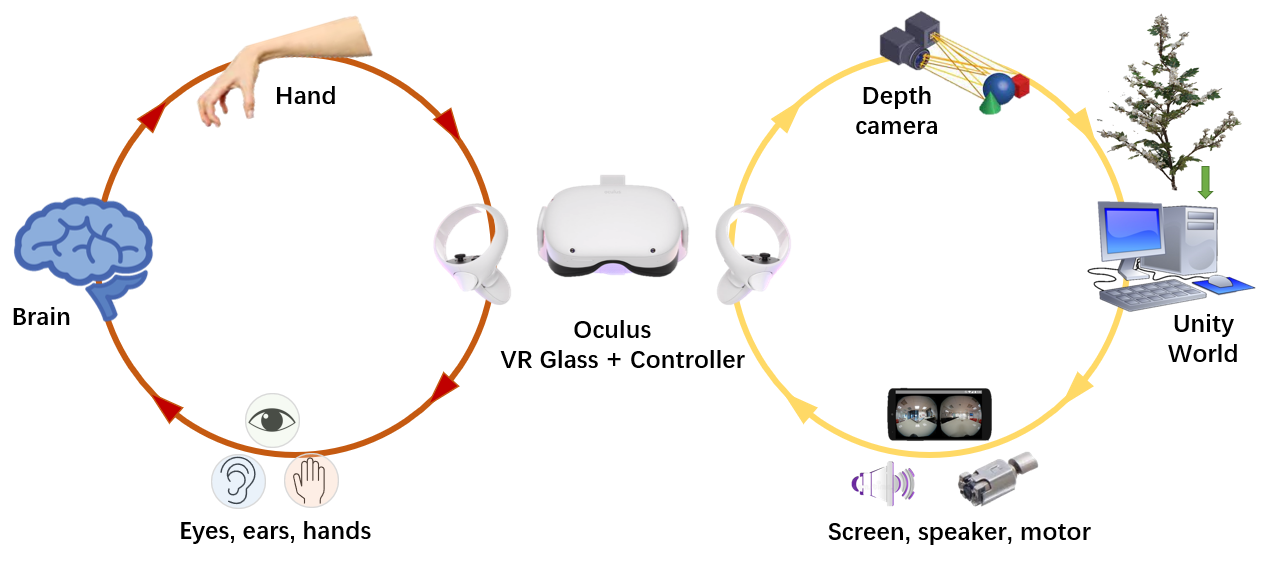
In order to achieve advance training for new employees, I will restore the actual orchard environment in a virtual 3D environment with movement and interaction in the virtual environment. At the same time research on how effective cues provide stimulus feedback in the simulated environment is necessary to train efficiency.
Schematic
Virtual environment software using Unity, using Mate’s Oculus to achieve virtual reality interaction.
- First I collected a number of fruit trees in the orchard 3D model will be imported into Unity to create a virtual orchard environment, and through the Oculus VR glasses to present the 3D environment to people.
- The person moves by hand holding the controller’s dual joystick, while the controller’s pose is also recognized by the depth camera on the VR glasses and converted into a human hand model.
- People can touch the flower clusters in the simulated environment to achieve the learning of flower thinning skills, while feedback is provided through object color changes, speakers, and vibrating motors.
Experimental Method
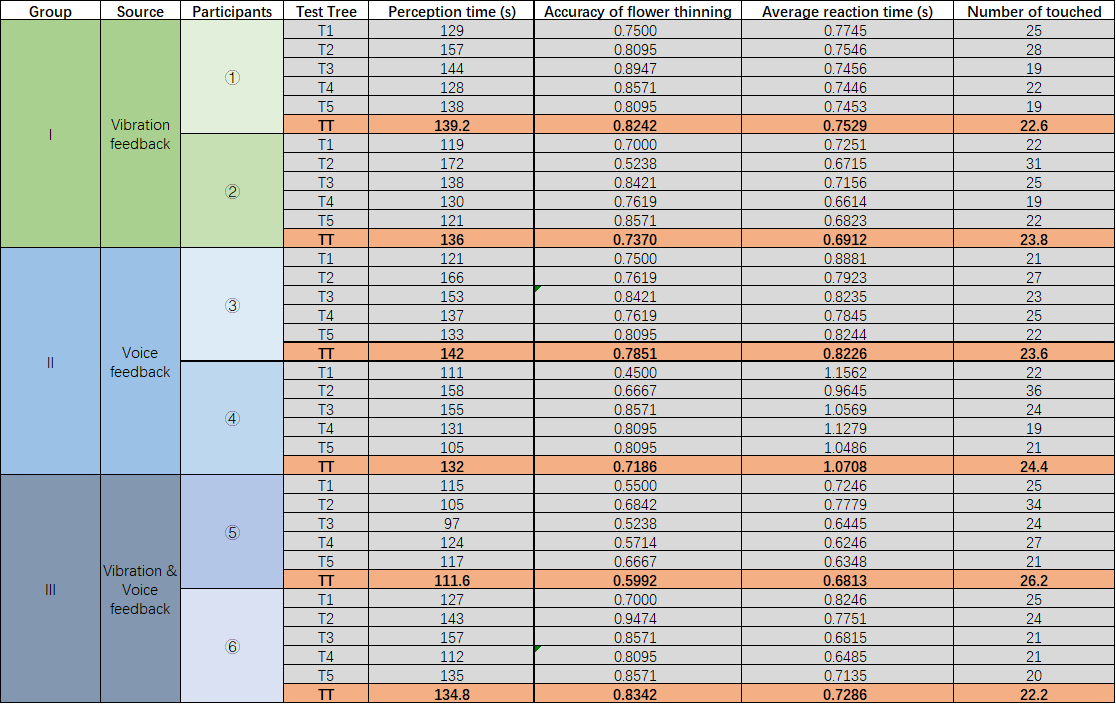
The participants were six people (male/ 20-30 years old) from different backgrounds. They were divided into three groups of two participants each. All participants were naive to the experiment and the equipment. They had normal vision and no physical problems.
The most important thing in flower thinning is to consider which flower clusters need to be removed. In this experiment, touching the flower clusters to be removed by hand recognition is defined as the task.
Experimental Design
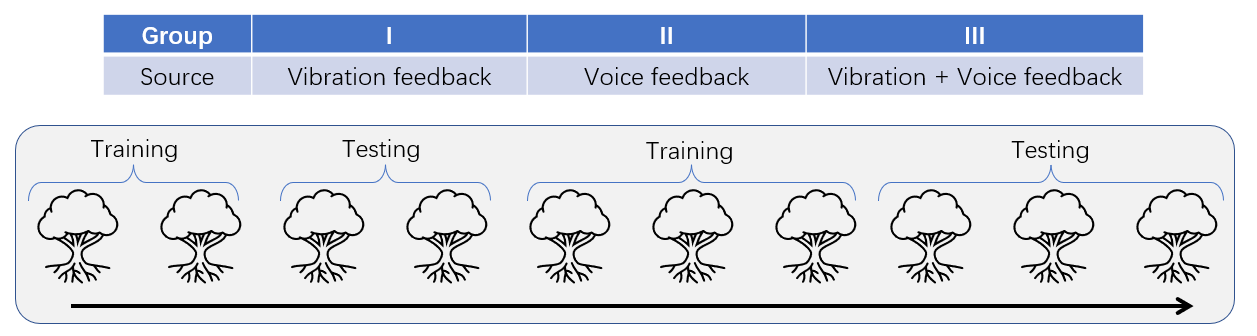
The experiment was divided into three groups, and the stimulus feedback for each group was: vibration feedback, voice feedback, and vibration & voice feedback. Each person will have 10 trees to train and learn, and the 10 trees are divided into two modes.
- In the training mode, the person needs to follow the color cues to touch the flower clusters.
- In the test mode, there will be no cues to judge for yourself.
- The feedback intensity is adjusted according to the per capita acceptable value.
Test Environment
As shown in the figure below, you need to follow the order of the red arrows for training and learning.

For the training tree of ①②⑤⑥⑦, we need to follow the guidance of the cue ball to touch, the original color is red, and blue after successful touching.

For the test tree of ③④⑧⑨⑩, we need to touch it according to our own judgment, and it is green when successfully touched.

Data Collection
In order to be able to fully understand the experimental procedure, I will collect the following data for subsequent analysis.
- The time it takes for participants to complete the experiment, a parameter that reflects the level of skill acquisition and speed of response.Perception time():
- Flower thinning accuracy rate(), used to assess participants’ mastery of the skil.
- Average reaction time(), used to assess participants’ reaction time to feedback stimuli.
The following table shows all the data collected during the experiment:
Data Analysis
First I visualize all experimental data.
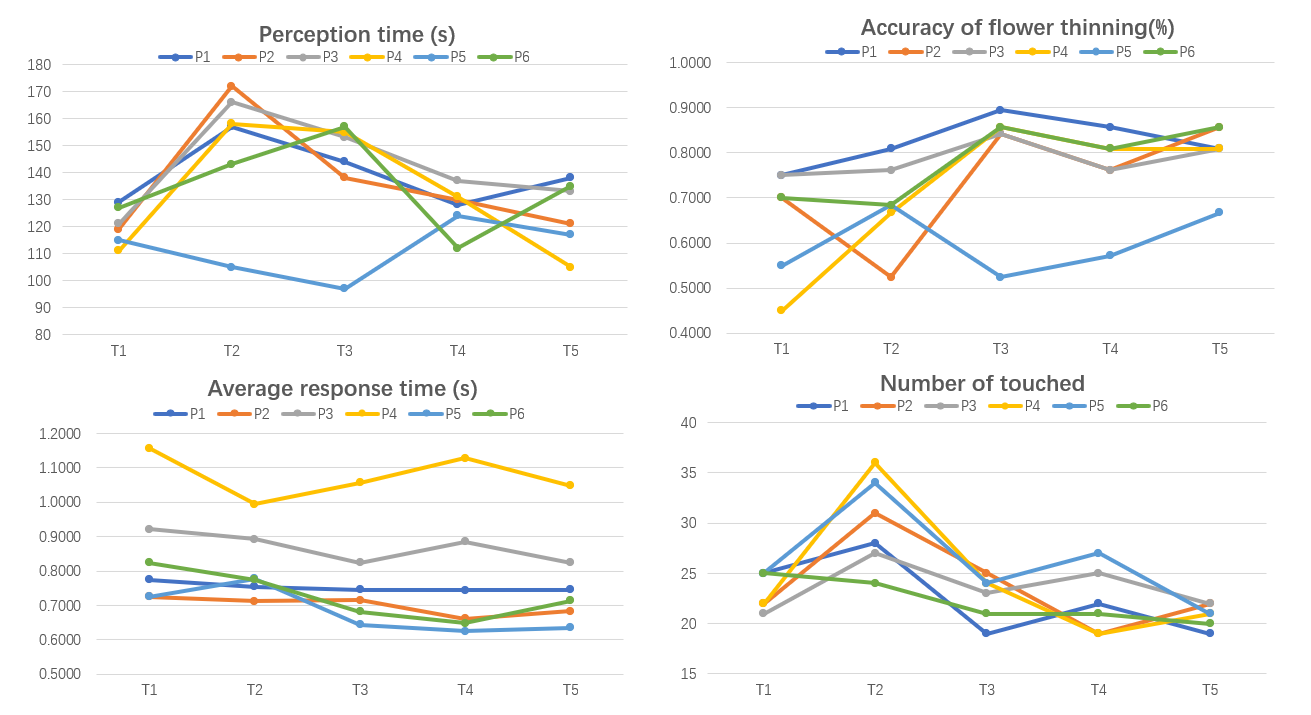
Average reaction time
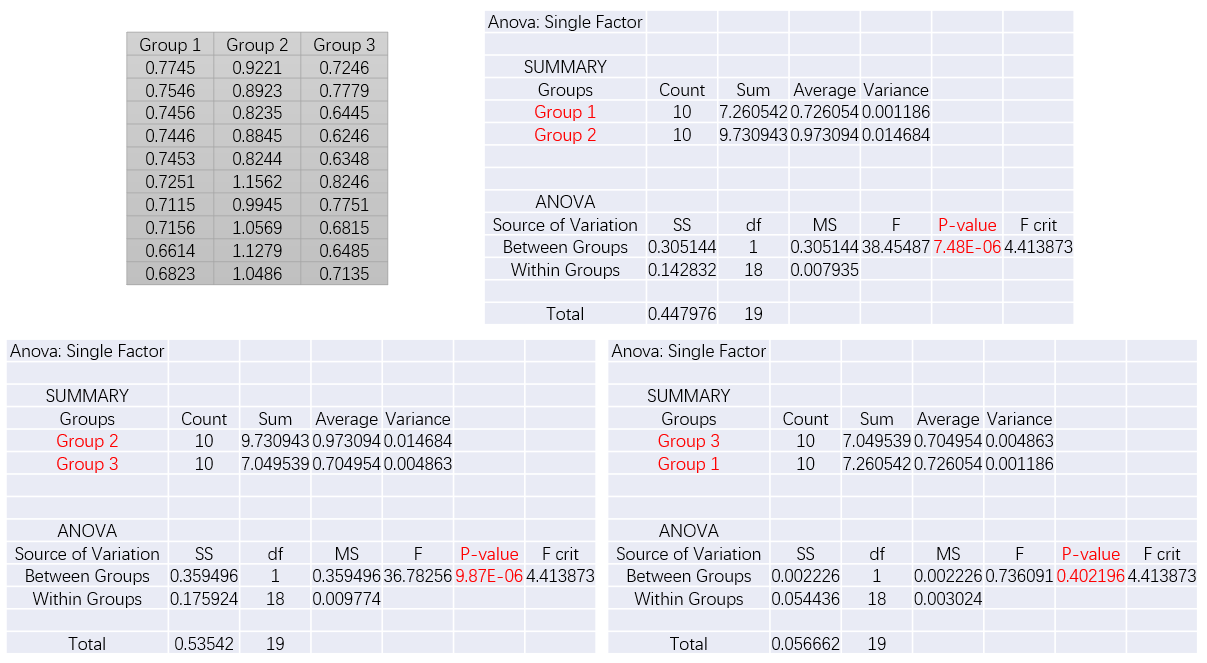
From the above graph we can clearly find the variability of the Average reaction time among the groups.
Analyzing the single-factor ANOVA by group, I found that the P-values for group 2 and group 1/3 were much less than 0.05, indicating a significant difference.
Perception time()
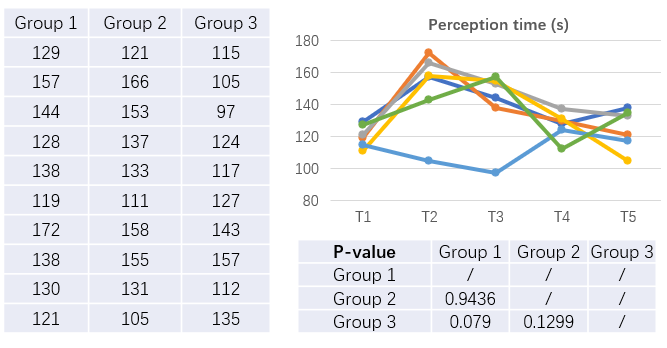
In the analysis of variability in perceived time, I did not find significant differences between the groups.
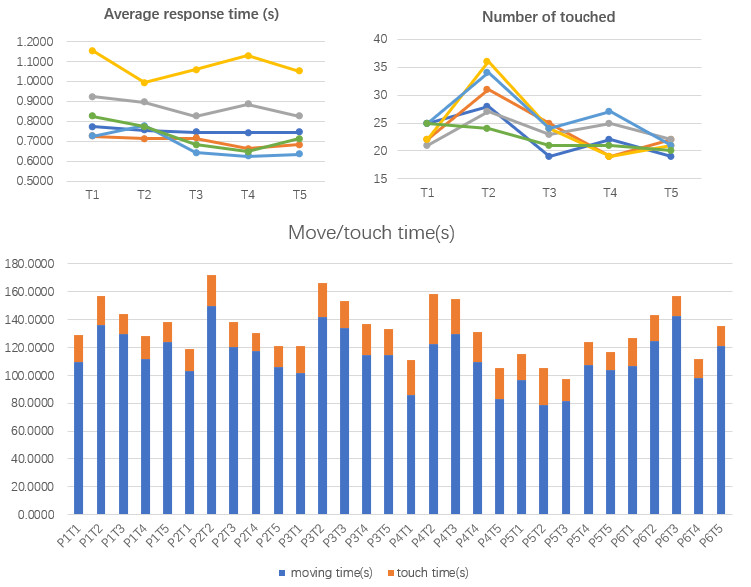
However, we found significant differences in the average reaction time, so I divided the perception time into two parts, one for participant controlled** movement and thinking time**, and the other for touch time. The following bar chart shows that touch time only accounted for about 15% of the overall time, so the effect of feedback stimuli on perceived time was extremely weak.
Flower thinning accuracy rate()
In the analysis of flower thinning accuracy, I found that participants improved their accuracy as they continued to understand and master how to thin flowers as they progressed through the training. However, no effect of different feedback stimulus sources was found in the single-element ANOVA.
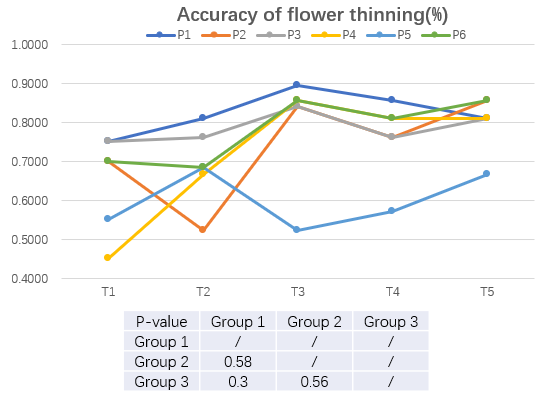
I considered whether it was the perception time spent by participants that could affect accuracy. I performed a correlation analysis between the time participants spent on each of the test trees and the accuracy of flower thinning.Weak correlations can be found in the following table for individual groups, but no overall correlation can be found between them.
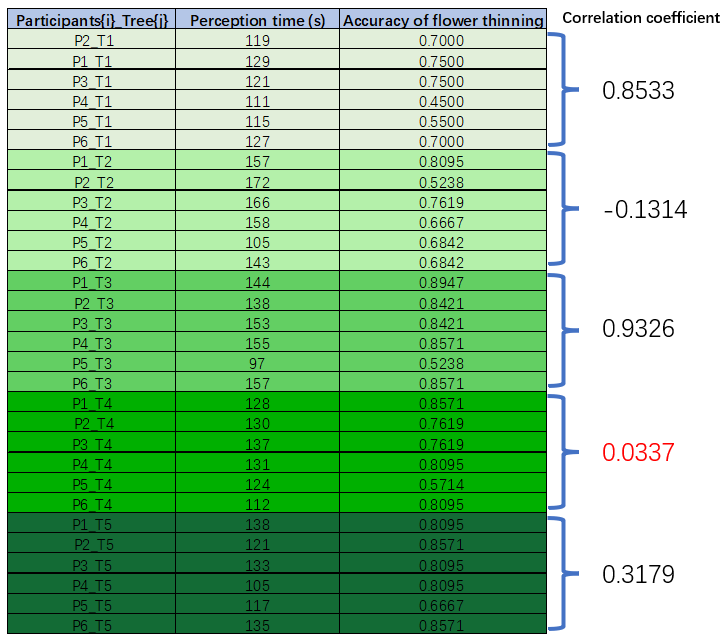
Conclusion
- Different sources of feedback have a significant effect on the average reaction time, vibration feedback better than voice feedback. This is because the operator holds the controller, his attention is on the vision and the hands, and the response to the vibration of the controller is faster.
- The touch feedback time is short and has no effect on the overall completion time. It is more affected by personal subjective judgment time.




评论区